In today’s fast-paced business world, efficiency and seamless coordination across departments are more important than ever.
That’s where ERP, or Enterprise Resource Planning, comes into play. But what does ERP really stand for, and why is it a cornerstone for modern organizations?
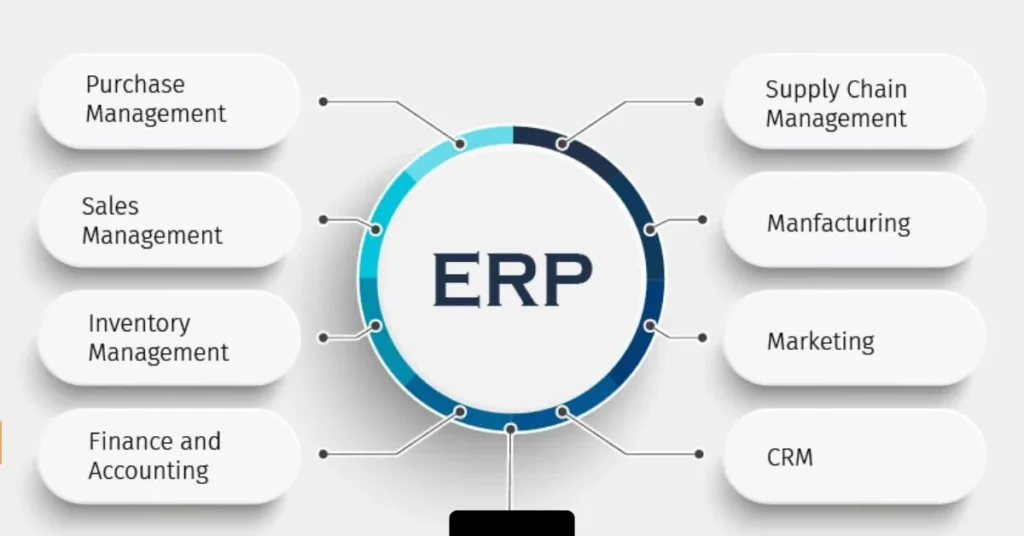
At its core, ERP is a comprehensive software system designed to integrate and manage key business processes from finance and human resources to inventory and customer relationships all in one centralized platform.
By connecting every department, ERP provides businesses with real-time insights, streamlined operations, and improved decision-making, helping them stay competitive in a constantly evolving market.
Whether you’re a small business exploring growth opportunities or a large enterprise looking to optimize operations, understanding ERP is crucial.
This guide will break down the meaning of ERP, how it works, its benefits, and why adopting the right ERP system can transform your organization’s productivity and efficiency.
What ERP Stands For
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning, a term that may sound simple but carries significant importance in the business world. Breaking it down helps to understand its full meaning.
Enterprise refers to the organization or business as a whole. It highlights that ERP is not just for a single department it’s designed to serve the entire organization, connecting all functions under one system.
Resource includes everything a business uses to operate effectively, such as employees, finances, materials, equipment, and data. ERP systems ensure that these resources are used efficiently and tracked accurately across departments.
Planning emphasizes the strategic aspect of ERP. It’s about coordinating resources to achieve business goals, reduce waste, and optimize operations. With proper planning, organizations can anticipate challenges, allocate resources smartly, and streamline processes for maximum productivity.
In practical terms, ERP is a software solution that integrates core business processes into one unified system. For example, a manufacturing company can use ERP to manage inventory levels, schedule production, track orders, and generate financial reports all from a single platform. This integration eliminates duplicated work, reduces errors, and provides managers with real-time insights to make informed decisions.
Understanding what ERP stands for is the first step to realizing its potential. By connecting enterprise, resources, and planning, ERP transforms how organizations operate, paving the way for efficiency, growth, and informed decision-making.
How ERP Works
ERP, or Enterprise Resource Planning, works by centralizing all critical business processes into a single, integrated system. At its core, an ERP system uses a centralized database where all departments finance, human resources, supply chain, inventory, sales, and customer relations can store and access information in real-time. This centralization eliminates data silos, reduces errors, and ensures consistency across the organization.
An ERP system typically includes different modules, each designed to manage specific functions. For instance, the finance module handles accounting, budgeting, and reporting, while the HR module manages payroll, recruitment, and employee records. The inventory and supply chain modules track stock levels, shipments, and orders, ensuring that products are delivered on time. Meanwhile, the CRM module allows businesses to manage customer interactions, sales pipelines, and support requests efficiently.
One of the most significant advantages of ERP is automation. Routine tasks like generating invoices, tracking orders, or updating inventory are handled automatically, freeing employees to focus on higher-value work. ERP also provides real-time reporting and analytics, giving managers an accurate, up-to-date view of operations. This data-driven approach helps businesses make informed decisions, optimize resources, and respond quickly to market changes.
In short, ERP works by connecting every part of an organization. Its integration, automation, and real-time insights allow businesses to operate more efficiently, reduce errors, and make strategic decisions that support growth and productivity.
Importance of ERP in Businesses
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) has become a cornerstone for businesses of all sizes because it streamlines operations and improves overall efficiency. By integrating multiple business functions into a single system, ERP ensures that departments no longer operate in isolation. This connectivity leads to better collaboration, faster communication, and reduced errors across the organization.
One of the key benefits of ERP is enhanced efficiency and productivity. With automated workflows, repetitive tasks such as data entry, report generation, and inventory tracking are handled seamlessly, freeing employees to focus on strategic tasks. Businesses also gain real-time insights into their operations. Managers can access up-to-date information on sales, production, finance, and customer interactions, enabling informed and timely decision-making.
ERP also helps in reducing costs and maximizing resource utilization. By providing a clear view of available resources, inventory levels, and production schedules, ERP minimizes waste, prevents stockouts, and avoids overproduction. This is particularly valuable for industries like manufacturing and retail, where efficient resource management directly impacts profitability.
Additionally, ERP supports scalability. As businesses grow, ERP systems can adapt to handle increased data, additional departments, and new business processes without compromising efficiency. It also ensures compliance with industry standards and regulations by maintaining accurate records and audit trails.
In today’s competitive market, implementing an ERP system is no longer optional it is essential. By improving efficiency, providing actionable insights, reducing costs, and supporting growth, ERP empowers businesses to stay agile, competitive, and ready for the future.
Types of ERP Systems
ERP systems come in several types, each designed to meet the unique needs of businesses. Choosing the right type is essential to ensure smooth operations, scalability, and a return on investment.
1. On-Premises ERP:
On-premises ERP systems are installed locally on a company’s servers and managed by its IT team. This type offers complete control over data and security, making it ideal for businesses with strict compliance requirements. Companies can customize the software extensively to match their specific processes. However, on-premises ERP typically requires higher upfront costs for hardware, licenses, and ongoing maintenance.
2. Cloud-Based ERP:
Cloud ERP systems are hosted on the vendor’s servers and accessed over the internet. They offer flexibility, lower upfront costs, and easier scalability, as businesses can adjust resources according to growth. Updates and maintenance are managed by the vendor, reducing IT workload. Cloud ERP is ideal for businesses seeking mobility, as employees can access the system anytime, anywhere.
3. Industry-Specific ERP:
Some ERP systems are tailored for specific industries, such as manufacturing, retail, healthcare, or education. These systems include pre-built modules and workflows designed to address industry challenges, such as production scheduling for manufacturing or patient management for healthcare.
4. Open-Source vs. Proprietary ERP:
Open-source ERP allows businesses to modify the source code to fit their requirements, offering flexibility and lower licensing costs. Proprietary ERP is developed and maintained by a vendor, providing full support, stability, and regular updates, but at a higher cost.
Understanding the types of ERP systems helps organizations select the right solution based on their size, industry, budget, and long-term goals, ensuring maximum efficiency and return on investment.
Popular ERP Software
There are numerous ERP software solutions available today, each designed to meet different business needs. Choosing the right one can significantly impact efficiency, productivity, and growth.
1. SAP
SAP is one of the most widely used ERP systems, especially among large enterprises. It offers comprehensive modules for finance, human resources, supply chain management, and customer relationship management. SAP is known for its robust functionality, scalability, and industry-specific solutions, making it ideal for global organizations with complex operations.
2. Oracle NetSuite
Oracle NetSuite is a cloud-based ERP solution popular with mid-sized and growing businesses. It integrates financial management, CRM, e-commerce, and supply chain operations. Its cloud-based nature allows real-time data access, seamless updates, and scalability, making it ideal for companies expanding rapidly.
3. Microsoft Dynamics 365
Microsoft Dynamics 365 combines ERP and CRM functionalities in a flexible, cloud-friendly platform. It is suitable for businesses of all sizes and offers modules for finance, sales, operations, and customer service. Integration with other Microsoft tools like Office 365 makes it user-friendly and highly adaptable.
4. Odoo
Odoo is an open-source ERP system that offers a wide range of modules, including accounting, inventory, sales, and project management. Its open-source nature allows businesses to customize and extend features to match specific needs. Odoo is particularly attractive for small to medium-sized enterprises due to its affordability and flexibility.
Each of these ERP systems has unique strengths, and the choice depends on business size, industry, budget, and specific operational requirements. Evaluating the features, scalability, and support of each solution ensures that companies select the right ERP system to improve efficiency, reduce errors, and support growth.
Benefits and Challenges of ERP
Implementing an ERP system can transform a business, offering a wide range of benefits while also presenting certain challenges that organizations need to manage carefully.
Benefits of ERP:
- Improved Efficiency: ERP automates repetitive tasks such as invoicing, payroll, and inventory updates, freeing employees to focus on strategic work.
- Centralized Data: All departments access the same information in real-time, reducing errors and data duplication.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Managers gain real-time insights into sales, finances, and operations, enabling faster and more informed decisions.
- Cost Savings: By optimizing resources, reducing waste, and improving productivity, ERP can significantly lower operational costs.
- Scalability: ERP systems grow with the business, accommodating more users, departments, and complex workflows as needed.
Challenges of ERP:
- High Implementation Cost: On-premises ERP and large-scale solutions often require substantial initial investment.
- Complexity: ERP systems can be complicated to set up, especially for large organizations with unique processes.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist adopting new systems, slowing down implementation.
- Customization Limitations: Some ERP solutions may not fully align with specific business needs without costly modifications.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: Older systems may require additional work to integrate smoothly with a new ERP platform.
Overcoming Challenges:
Successful ERP implementation requires careful planning, training, and selecting the right system. Partnering with experienced vendors and starting with phased rollouts can help businesses maximize ERP benefits while minimizing risks.
ERP, when implemented thoughtfully, can be a powerful tool for efficiency, growth, and strategic decision-making, outweighing its potential challenges.
ERP Trends and Future Outlook
The world of ERP is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and the growing demand for more agile, data-driven business solutions. Understanding current trends helps organizations stay competitive and plan for future growth.
1. Cloud ERP: Cloud-based ERP systems continue to gain popularity due to their flexibility, scalability, and lower upfront costs. Businesses can access data anytime, anywhere, making remote work and global operations more efficient.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: Modern ERP solutions are integrating AI to analyze data, predict trends, and automate complex tasks. For example, AI can forecast inventory needs, detect anomalies in financial reports, and optimize resource allocation.
3. Mobile ERP: As employees demand access to business data on-the-go, mobile ERP apps are becoming essential. Mobile ERP allows managers and teams to update, monitor, and approve processes from anywhere, improving responsiveness and collaboration.
4. Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: IoT devices provide real-time data from machinery, vehicles, or inventory. ERP systems leveraging IoT can track assets, monitor production, and optimize supply chains with unprecedented accuracy.
5. Advanced Analytics and Reporting: ERP platforms increasingly offer powerful analytics tools, allowing businesses to gain deeper insights into performance metrics, customer behavior, and market trends.
Future Outlook: ERP is no longer just a back-office tool; it is becoming a strategic platform that drives decision-making, innovation, and digital transformation. Businesses adopting modern ERP technologies can streamline operations, reduce costs, and respond quickly to market changes, positioning themselves for sustainable growth in an increasingly competitive landscape.
FAQs About ERP
1. What is ERP used for?
ERP, or Enterprise Resource Planning, is used to integrate and manage core business processes. It helps organizations streamline workflows, automate tasks, and provide real-time insights into operations, finances, HR, supply chains, and customer interactions.
2. Who needs ERP?
ERP is valuable for businesses of all sizes, from small startups to large enterprises. Companies with multiple departments, complex operations, or ambitions for growth can benefit from ERP’s ability to connect functions and improve efficiency.
3. How much does ERP cost?
The cost of ERP varies based on system type, business size, and complexity. On-premises ERP usually requires higher upfront costs for hardware, software licenses, and maintenance, while cloud-based ERP operates on a subscription model, reducing initial investment. Additional costs may include implementation, customization, and staff training.
4. What is the difference between ERP and CRM?
While ERP focuses on internal business processes like finance, inventory, and HR, CRM (Customer Relationship Management) focuses on customer interactions, sales, and marketing. Many modern ERP systems include CRM modules for a fully integrated solution.
5. How to choose the right ERP system?
Choosing the right ERP depends on your business size, industry, budget, and goals. Consider factors like scalability, customization, cloud vs. on-premises, vendor support, and user-friendliness. Planning a phased implementation and consulting experts can also ensure a smooth transition.
6. Can small businesses benefit from ERP?
Yes. Cloud-based and modular ERP solutions make it affordable and flexible for small businesses, helping them compete with larger organizations by improving efficiency and providing insights for strategic decisions.
ERP answers essential business challenges by integrating processes, improving data visibility, and supporting growth, making it a critical tool for modern organizations.
Conclusion
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) has become an essential tool for businesses aiming to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and make data-driven decisions.
At its core, ERP integrates all critical business functions from finance and human resources to supply chain management and customer relations into a single, centralized system.
This integration allows companies to eliminate data silos, reduce errors, and enhance collaboration across departments.
The benefits of ERP are significant. Businesses gain real-time insights into operations, enabling faster and more informed decision-making.
Automation of routine tasks frees employees to focus on strategic initiatives, while accurate resource planning helps reduce costs and optimize productivity.
ERP systems are also scalable, meaning they can grow alongside a business, supporting expansion and adapting to new processes or markets.
However, successful ERP implementation requires careful planning, employee training, and choosing the right system based on organizational needs.
Companies must weigh factors such as cloud versus on-premises deployment, industry-specific requirements, and long-term scalability.
Despite these challenges, the advantages far outweigh the potential obstacles, making ERP a strategic investment for businesses of all sizes.
Looking ahead, ERP continues to evolve with cloud computing, AI, IoT, and mobile integration, transforming it from a back-office tool into a central platform for business strategy and innovation.
Organizations that adopt ERP effectively can gain a competitive edge, streamline operations, and achieve sustainable growth in today’s fast-paced business environment.

Jordon Fox is an emerging artist and creative from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, known for blending music, fashion, and fitness into his personal brand and artistic identity. He’s built a reputation as a multi-talented creator with a strong focus on authenticity and inspiring others.